Exploring the North American Pitcher Plant Ecology

Intro
The North American Pitcher Plant holds a unique position in the ecological tapestry of its native environments. Its specialized structure allows it to thrive in nutrient-poor soils, showcasing an extraordinary adaptation strategy. This intriguing carnivorous plant plays a pivotal role in its habitat, forming symbiotic relationships with various organisms and contributing to biodiversity. Understanding the ecology of the Pitcher Plant is not only essential for preserving this species but also for grasping broader ecological interactions within its environment.
Overview of Forestry Practices
Importance of Foresting
Forestry practices are critical for maintaining healthy ecosystems. They contribute to biodiversity, carbon sequestration, and the preservation of soil and water quality. The sustainable management of forests ensures that they continue to provide essential resources, such as timber and non-timber products, while supporting diverse biological communities. The North American Pitcher Plant finds its habitat in these ecosystems, often in wetlands and bogs, underscoring the importance of responsible forestry practices to maintain such environments.
Types of Forestry Practices
Different types of forestry practices influence ecological systems. Some of the key practices include:
- Selective Logging: This method allows certain trees to remain while harvesting others, preserving the broader ecosystem and minimizing disruption.
- Clear-Cutting: While often criticized for its impact, when utilized properly, it can create space for new growth and regeneration.
- Agroforestry: Integrating trees with crops can enhance biodiversity and soil fertility, providing benefits to both agriculture and forestry.
Each method has its merits and drawbacks, and comprehension of these practices is fundamental for integrating sustainable techniques that support species like the Pitcher Plant.
Best Practices for Sustainable Woodland Stewardship
Principles of Sustainable Forestry
Sustainable forestry balances ecological integrity, economic viability, and social equity. Some of the fundamental principles include:
- Ecosystem-Based Management: This approach considers the forest as a complex ecosystem, emphasizing ecological processes and interactions.
- Adaptive Management: Flexibility in management strategies allows for adjustments based on ecological changes or emerging scientific understanding.
- Community Engagement: Collaboration with local communities and stakeholders is essential for informed decision-making and effective conservation strategies.
Adhering to these principles can enhance the health of forests where the Pitcher Plant resides, ensuring that it continues to thrive amid changing environmental conditions.
Techniques for Land Management
Effective land management techniques contribute to the sustainability of woodland areas. Some techniques include:
- Buffer Strips: Maintaining undisturbed areas around water bodies to protect water quality and prevent erosion.
- Controlled Burns: Utilizing fire to manage understory plants and maintain ecosystem health can promote the growth of specific species, including the Pitcher Plant.
- Reforestation: Planting native species helps restore habitats that support diverse wildlife and plant communities.
Incorporating these techniques fosters healthy ecosystems that enable species adaptation and conservation.
Innovative Techniques in Forestry
Latest Technological Advancements
Modern technology plays a vital role in forest management and conservation. Innovations such as drone mapping, remote sensing, and geographic information systems (GIS) provide valuable data for forest monitoring and assessment. These tools help in understanding land use changes, assessing ecosystem health, and planning conservation efforts tailored to specific habitats where plants like the North American Pitcher Plant grow.
Integrating Traditional Knowledge with Modern Science
Combining traditional ecological knowledge with scientific research enhances forestry practices. Indigenous communities often possess valuable insights into local ecosystems that can inform sustainable management approaches. Collaborative efforts between traditional knowledge holders and scientific communities can lead to more effective conservation strategies. For instance, recognizing patterns of plant growth and habitat preferences from indigenous perspectives can prove invaluable in the context of managing the North American Pitcher Plant's habitat.
Key Insight: Effective conservation of species like the North American Pitcher Plant requires a thoughtful integration of scientific understanding and traditional ecological practices to create resilient ecosystems.
Understanding these facets of forestry practices establishes a foundation for further exploration of the North American Pitcher Plant's ecology and significance.
Prelims to the North American Pitcher Plant
The North American Pitcher Plant is not merely an intriguing species; it serves as an essential component of its ecosystem. Understanding its characteristics helps comprehend the complexities of biodiversity in its habitats. This section explores the unique elements that define this plant, its adaptation strategies, and its contribution to ecological health.
Overview and Distinctive Features
The North American Pitcher Plant, primarily represented by the genus Sarracenia, encompasses several species notable for their distinct morphology. These plants are recognized for their tubular leaves that trap and digest prey, a feature suited to the nutrient-poor soils in which they thrive. These adaptations highlight a fascinating aspect of evolutionary biology, underscoring the relationship between organism and environment.
The colors and shapes of pitcher plants vary, with some sporting vibrant hues that lure insects. The structure of their leaves includes a modified leaf that forms a deep cavity filled with liquid. Here, the plant attracts its prey, primarily insects, which fall into the fluid and cannot escape. This method of nutrient acquisition is vital for their survival in acidic bogs where soil nutrients are scarce.
Historical Significance in Native Cultures
Historically, the North American Pitcher Plant has drawn the interest of various Native American tribes. In these cultures, the plant was not only a subject of wonder but also a resource for medicinal purposes. Some tribes utilized the plant's features for treating ailments, tapping into the deep knowledge of local flora. This historical context emphasizes the relevancy of the Pitcher Plant in discussions about cultural heritage and ecological respect.


The recognition of the plant's role in traditional practices brings forth an appreciation for indigenous knowledge systems. They understood the importance of balance in ecosystem interactions, valuing plants such as the North American Pitcher Plant for their both ecological and cultural roles.
"The North American Pitcher Plant is a testament to nature's ingenuity and an important symbol of the interdependence of plants and their environments."
Taxonomy and Classification
Taxonomy and classification are crucial in understanding the North American Pitcher Plant’s role in its ecosystem and its relationships with other species. Proper classification allows scientists and ecologists to identify and differentiate between various species. This in turn guides conservation strategies and ecological studies. Taxonomy highlights the diversity within the genus, showcasing how different species adapt to distinct environments. Moreover, it contributes to our comprehension of evolutionary traits and the ecological niche that these plants occupy.
Genus and Species Identification
The North American Pitcher Plant is a member of the Sarraceniaceae family, primarily categorized under the Sarracenia genus. There are several species found in North America. These include Sarracenia purpurea, Sarracenia flava, and Sarracenia leucophylla. Each species shows unique morphological traits, which aid in their identification.
- Sarracenia purpurea: Recognized by its purple-tinged tubular leaves, this species is often found in wetlands.
- Sarracenia flava: Known for its tall, yellow flowers and is commonly seen in bogs.
- Sarracenia leucophylla: Features striking white and green leaves, attracting attention due to its beauty.
Identifying these species is not merely academic; it has significant implications in conservation biology. Misidentification can lead to ineffective conservation efforts. Hence, accurate knowledge of genus and species is essential.
Phylogenetic Relationships
Studying the phylogenetic relationships among North American Pitcher Plants helps to elucidate their evolutionary history. Phylogenetics examines the evolutionary connections between different plant species, offering insights into common ancestors and the genetic variability within the Sarracenia genus.
For instance, the genetic adaptations that allow some species to thrive in acidic, nutrient-poor soils inform conservation practices. Understanding which traits are inherited among species can shape selective breeding programs aimed at increasing resilience against environmental changes.
Furthermore, phylogenetic analyses assist in mapping out the evolutionary trajectories of these plants. They can provide context on how specific adaptations have emerged in response to ecological pressures. With ongoing habitat loss, comprehending these relationships is vital. It emphasizes how interconnected species are and how conservation efforts can protect not only individual plants but their entire ecosystems.
"An in-depth grasp of taxonomy and phylogenetic relationships is necessary for preserving the intact ecosystems that North American Pitcher Plants inhabit."
This understanding eventually contributes to broader ecological conservation initiatives, bridging the gap between scientific research and practical conservation efforts.
Morphological Adaptations
Morphological adaptations of the North American Pitcher Plant are central to its survival and functionality within its ecosystem. These adaptations enable the plant to thrive in nutrient-poor environments by developing specialized structures that aid in both nutrient acquisition and moisture retention. Understanding these features contributes to our knowledge of plant ecology and emphasizes the significance of conservation strategies.
Leaf Structure and Functionality
The leaves of the Pitcher Plant are its most distinguishing feature. Each leaf develops into a tubular shape, resembling a pitcher, which is why the plant is named as such. This structure serves a dual purpose. Firstly, it acts as a container that attracts and traps insects. The internal surfaces of these leaves are lined with a slippery layer that makes it difficult for prey to escape once they fall in. The unique coloration and nectar-secreting glands located at the rim of the pitcher attract unsuspecting insects, enhancing the likelihood of trapping.
In addition to trapping insects, the leaf structure also plays a vital role in water management. The cylindrical shape allows for the efficient collection of rainwater, which helps in maintaining hydration during drier periods. This adaptation is crucial, especially in wetlands where the water table may fluctuate seasonally. Through their specialized leaf structure, North American Pitcher Plants can gather both nutrients and moisture, thus sustaining their growth in challenging environmental conditions.
Trap Mechanisms and Digestive Processes
The trap mechanisms of the North American Pitcher Plant are intricate. When insects fall into the pitcher, they may find it difficult to escape due to the walls' smooth nature. The design evolved to maximize the entrapment efficiency. Furthermore, the plant secretes digestive enzymes to break down the captured insects, allowing it to absorb essential nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorous, which are often limited in its natural habitats.
Once caught, the insects are digested over time through a series of chemical reactions facilitated by the enzymes. This digestive process is crucial for the plant's survival, as it supplements the nutrient intake, allowing the Pitcher Plant to thrive in nutrient-poor soils.
The adaptations of the North American Pitcher Plant, particularly its leaf structure and trap mechanisms, showcase a remarkable evolutionary strategy to acquire nutrients in a specialized ecological niche.
In summary, the morphological adaptations of the North American Pitcher Plant not only define its identity but also play a vital role in its survival. They reflect the plant's ability to compete successfully in its environment while illustrating the intricate connections within ecosystems.
Habitat and Distribution
Understanding the habitat and distribution of the North American Pitcher Plant is crucial for comprehending its ecological roles and conservation needs. The Pitcher Plant, with its unique adaptations, thrives in specific environments that support its growth and reproductive success. This elucidation of habitat preferences ushers in appreciation for its role in maintaining biodiversity.
Preferred Ecosystems and Soil Conditions
The North American Pitcher Plant primarily inhabits wetlands, including bogs, fens, and swampy areas. These ecosystems often have unique hydrological conditions, characterized by poorly drained soils and high moisture levels. The importance of such environments cannot be understated. They serve as nurseries for various species and act as crucial water filtration systems, thereby promoting ecological health.
The soil conditions important for the growth of the Pitcher Plant typically include:
- Acidic pH levels: The plants thrive in soils that range from moderately acidic to very acidic. This pH range supports the specific microbial communities critical for nutrient absorption.
- Low nutrient availability: The North American Pitcher Plant is adapted to nutrient-poor conditions, drawing nutrients primarily from prey rather than soil.
- Saturated substrates: A high water table is essential for its survival, as it prefers constantly moist soil.
This combination of soil characteristics and wetland ecosystems forms a habitat that not only sustains Pitcher Plants but also enriches biodiversity, supporting multiple plant and animal species.
Geographical Range Across North America
The geographical distribution of the North American Pitcher Plant is concentrated in specific regions across the continent. These areas predominantly include the eastern United States and Canada, with notable populations found in the following states:


- Florida: Home to several species, including the widely recognized Sarracenia flava.
- North Carolina: The moist lowlands provide an ideal environment for these plants.
- Virginia: Rich in diverse ecosystems, promoting population density of Pitcher Plants.
- Alabama and Mississippi: These states have favorable climatic conditions that support the growth of various Sarracenia species.
According to recent studies, the distribution of Pitcher Plants appears to be shrinking due to habitat loss caused by human activities such as urban development and agricultural expansion. This geographical aspect not only highlights the beauty of their current habitats but also underscores the urgency to avert further loss to stabilize existing populations and restore habitats.
"Conservation strategies focusing on habitat preservation are essential to enshrine the future of the North American Pitcher Plant and its unique wetland ecosystems."
Protecting these critical habitats and understanding their distribution is key to ensuring that the ecological significance of the North American Pitcher Plant is maintained. Such insights can guide effective conservation policies and practices geared toward habitat restoration and management.
Ecological Interactions
The ecological interactions surrounding the North American Pitcher Plant are multifaceted and essential for understanding its role within its environment. These interactions with insects and other plant species contribute to the overall health of the ecosystem. They enhance biodiversity, establish complex food webs, and aid in nutrient cycling, ensuring the survival not only of the pitcher plant itself but also of numerous other organisms that share its habitat.
Symbiotic Relationships with Insects
The North American Pitcher Plant has developed distinctive mechanisms to lure and capture insects. This relationship is largely symbiotic, where both the plant and the insects benefit, although in unequal measures. Insects, particularly those belonging to the order Hymenoptera, are attracted to the bright colors and sweet nectar of the plant. Upon entering the pitcher, they encounter a slippery inner surface which makes escape nearly impossible.
- Nutrient Acquisition: The main benefit to the pitcher plant is nutrient acquisition. As insects decompose within the pitcher, they release nitrogen and other essential compounds usable by the plant. This is particularly crucial in nutrient-poor environments where the plant often resides.
- Decomposition Processes: The decomposition process inside the pitcher also creates an environment ripe for microbial activity, which can further break down materials and release nutrients. Thus, the pitcher plant becomes both a trap and a nutrient-processing chamber in its ecosystem.
- Pollinator Support: Some insects, after feeding and sometimes escaping from the plant, become pollinators, assisting in the reproductive processes of plants nearby. This interlinking promotes plant diversity and ecological balance in the region.
"The unique design of the pitcher plant not only facilitates predator capture but also enhances its survival in nutrient-deficient soils."
Interactions with Other Plant Species
The North American Pitcher Plant does not exist in isolation. It interacts with other plant species, which can be both competitive and cooperative. These relationships are critical for the balance of the ecosystem.
- Competition for Resources: Pitcher plants often inhabit wetlands and bogs, areas where resources can be scarce. They may compete with other plant species for sunlight and space. The ability of pitcher plants to attract insects gives them an advantage in nutrient uptake, allowing them to thrive even in harsh conditions where other plants may struggle.
- Facilitation of Habitat: Some species of plants can provide shade, thereby reducing evaporation and maintaining moisture levels in the soil, an essential aspect for the pitcher plant's survival. These neighboring plants can create a microhabitat supporting the tender growth of shoots and roots.
- Community Dynamics: The presence of pitcher plants can affect the assemblage of other species. For instance, the decaying organic material from trapped insects may alter soil pH and nutrient levels, affecting nearby plants' growth patterns.
Understanding these ecological interactions highlights the complexities within which the North American Pitcher Plant operates. It emphasizes the importance of conservation efforts by illustrating how this singular plant not only survives but fosters liveliness in its wetland communities.
Conservation Status
The conservation status of the North American Pitcher Plant is a crucial aspect of understanding its ecology and significance. As a species that thrives in specific habitats, it faces numerous challenges that threaten its existence. The decline of populations due to habitat loss and environmental changes calls for immediate attention and decisive actions. These factors not only impact the Pitcher Plant but also affect the broader ecosystems in which they reside.
Recognizing the importance of conservation for this species helps in preserving the biodiversity within wetland ecosystems. It provides valuable insights into how plant species can adapt to specific environmental conditions while also sustaining complex food webs. Protecting the North American Pitcher Plant promotes ecological health, which is beneficial not just for the species itself but for a multitude of organisms relying on these habitats.
Threats to Habitat and Population
Threats to the North American Pitcher Plant's habitat and population are numerous and varied. Here are some significant factors contributing to the decline:
- Habitat Loss: Urban development and agricultural expansion result in the destruction of the wetlands where these plants typically grow. These alterations lead to a fragmented environment, making it difficult for populations to thrive.
- Pollution: The introduction of chemicals and waste into aquatic systems can severely impact the Pitcher Plant's ability to grow and reproduce. Pollutants can alter soil chemistry and water quality, affecting the plant's nutrient absorption.
- Climate Change: Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns disrupt the delicate balance of the ecosystems where the Pitcher Plant exists. Increased drought or flooding can jeopardize the growth conditions necessary for its survival.
- Invasive Species: Non-native plants and animals can outcompete the Pitcher Plant for resources, thereby decreasing its chances of survival. Invasive species can alter habitat structure and the availability of nutrients.
The cumulative effect of these threats can lead to diminishing populations and increased vulnerability, highlighting the need for immediate intervention.
Conservation Efforts and Success Stories
Efforts to conserve the North American Pitcher Plant offer hope for its future. Various organizations and governmental bodies are collaborating on initiatives aimed at stabilizing and enhancing the populations of this unique species. Significant efforts include:
- Restoration Projects: Ecological restoration of wetlands focuses on re-establishing the natural habitats critical for the Pitcher Plant's growth. Such projects involve removing invasive species and improving water quality.
- Protected Areas: Designating specific regions as protected areas helps to safeguard the habitats where these plants flourish. Conservation easements allow for the protection of lands while permitting sustainable land use practices.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educating the public about the Pitcher Plant's role in the ecosystem fosters appreciation and encourages citizen science initiatives. Engaged communities can advocate for preservation efforts and participate in restoration activities.
- Research Initiatives: Ongoing scientific research is vital for understanding the impacts of climate change and habitat modifications. Data gathered helps inform conservation strategies and addresses the specific needs of the Pitcher Plant.
"Conservation is not just about protecting the species; it’s about preserving the intricate web of life they support."
These combined efforts reflect a commitment to ensuring the survival of the North American Pitcher Plant, recognizing its inherent value in maintaining biodiversity and ecological integrity.
Role in Ecosystem Services
The North American Pitcher Plant plays a pivotal role in its ecosystem, offering multiple services that enhance environmental health and biodiversity. Its unique adaptations not only allow it to thrive in nutrient-poor soils, but also support surrounding flora and fauna, showcasing its significance beyond mere survival. Recognizing and understanding these contributions can inform conservation efforts and promote awareness of the ecological interdependence within these habitats.
Contributions to Biodiversity
The presence of the North American Pitcher Plant is vital in maintaining biodiversity within its ecosystem. This plant attracts a variety of insects, which serve as both prey and pollinators. It acts as a trap for numerous insect species, aiding in population control and contributing to the food web. By providing a habitat for unique microorganisms, fungi, and other plant species, the Pitcher Plant fosters an intricate web of life.
Moreover, its carnivorous nature offers ecological benefits by helping to regulate insect populations that can become pests. This relationship highlights the significance of the Pitcher Plant as an integral part of its ecosystem, ensuring balance and diversity among species.
Soil and Water Filtration
Another crucial function of the North American Pitcher Plant is its ability to assist in soil and water filtration. The plant helps maintain soil health by accumulating organic matter and nutrients from its prey. As insects decompose within its trap, they enrich the surrounding soil, promoting plant growth and soil structure.
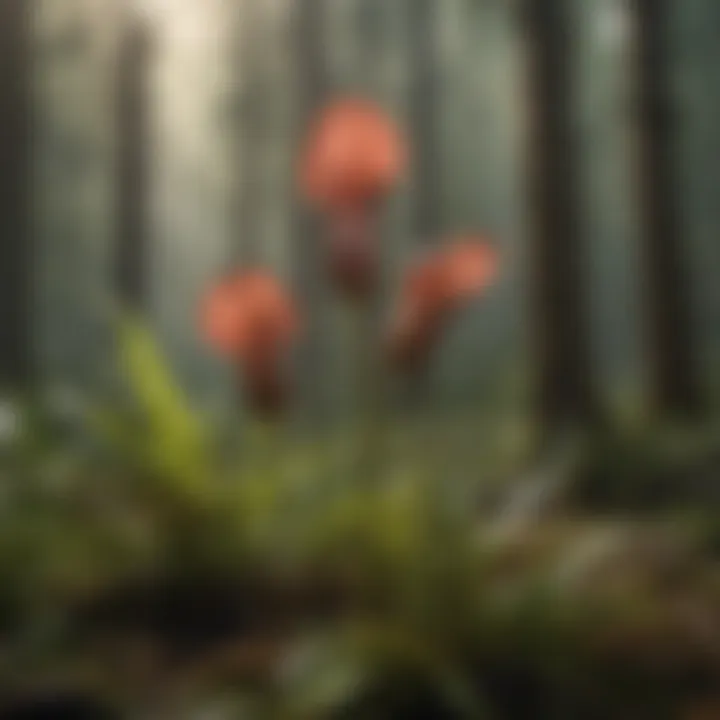
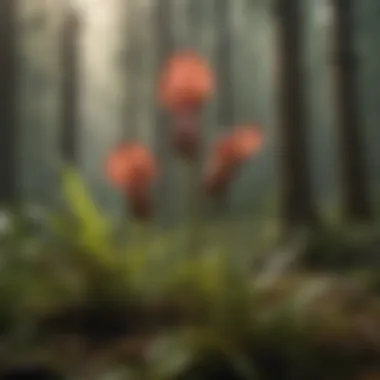

In terms of water filtration, Pitcher Plants facilitate the natural purification processes. Their specialized trap structure and biological activity contribute to reducing sediment and pollutants in water. This process helps maintain cleaner water bodies, ultimately supporting aquatic life and enhancing the overall ecosystem health.
"The Pitcher Plant stands as a natural filter and a crucial player in the dynamics of its habitat."
In summary, the roles of the North American Pitcher Plant in enhancing biodiversity and supporting soil and water filtration are essential. These ecosystem services are not merely byproducts of the plant’s existence but fundamental aspects that elevate its significance in the broader ecological landscape. Conservation efforts directed towards these plants benefit not only their populations but also the myriad of other species dependent on these critical services.
Cultural and Economic Importance
The North American Pitcher Plant is not only a fascinating species in terms of ecology but also holds significant cultural and economic value. This plant has been used in various aspects of traditional practices, while also emerging as an important component in the growing ecotourism sector. Understanding its importance allows for a deeper appreciation of the plant’s role in human culture and the economy.
Use in Traditional Medicine
Historically, the North American Pitcher Plant has been employed in traditional medicine by Native American tribes. The leaves and roots have been used for a range of ailments. Some practitioners believe that the plant possesses anti-inflammatory properties. It has been claimed that an infusion made from the leaves can help alleviate symptoms such as coughs and gastrointestinal issues.
Although modern science has only begun to explore these claims, the traditional knowledge surrounding the Pitcher Plant emphasizes its cultural role. Ethnobotanical studies suggest there is potential for developing new medicinal products inspired by these practices. Continued research could lead to uncovering valuable properties of the Pitcher Plant and integrating them more widely into contemporary herbal medicine.
Role in Ecotourism
Ecotourism is another dimension of the economic importance of the North American Pitcher Plant. Many protected wetlands and nature reserves highlight this unique plant as a key attraction. Tourists interested in biodiversity often seek regions where these plants thrive, contributing to local economies through eco-friendly tourism.
Professionals are recognizing the benefits of preserving habitats where the North American Pitcher Plant is found. Visitors engage in educational trips, contribute to local conservation efforts, and support businesses based on local culture and nature. This not only generates revenue but also fosters a greater awareness of environmental issues among tourists, creating a cycle of appreciation and stewardship.
In summary, the cultural and economic importance of the North American Pitcher Plant can be viewed through its traditional medical uses and its role in the ecotourism industry. Both aspects encourage conservation and highlight the need for sustainable practices that benefit both nature and local communities. As we navigate the future, recognizing and promoting these elements will be vital for the survival of such unique species and their habitats.
"Cultural understanding and economic opportunity can coexist, leading to conservation efforts that benefit all."
Engaging with the North American Pitcher Plant presents an opportunity to connect ecological integrity with cultural heritage, enhancing the value of this remarkable species.
Research and Education
Research and education are crucial facets in understanding the ecological importance of the North American Pitcher Plant. This plant is not only a unique species, but it also plays a significant role in its ecosystem. Through intensive research, we can gather data that informs conservation strategies and enhances our comprehension of biodiversity.
Scientific Studies and Findings
Scientific studies focusing on the North American Pitcher Plant have yielded critical insights into its biology and ecology. Research has shown that these plants are specialized carnivores, adapted to thrive in nutrient-poor soils. They obtain essential nutrients by capturing and digesting insects, which provides a deeper understanding of their ecological niche.
Additionally, studies have examined the symbiotic relationships that the Pitcher Plant maintains with various insect species. For example, certain ants are known to inhabit the plant, offering protection against herbivores, while the plant provides shelter and nutrients in return. Such findings shed light on the complex interdependencies within its habitat, highlighting how the plant contributes to and relies on biodiversity.
"Understanding the unique ecological roles played by species like the North American Pitcher Plant is vital for effective conservation efforts."
Moreover, research on the effects of climate change reveals how shifting temperatures and changing precipitation patterns may impact the habitat of the Pitcher Plant. Understanding these dynamics is essential for developing adaptive management strategies to preserve them for future generations.
Educational Programs and Outreach
Educational programs centered on the North American Pitcher Plant serve multiple functions. Firstly, they raise awareness about the importance of conserving native species and their habitats. Schools, universities, and environmental organizations can develop curriculums that integrate this plant into broader lessons on ecology and conservation.
Outreach programs can include workshop events and field trips to natural habitats where the Pitcher Plant grows. Engaging hands-on experiences allow participants to observe the plant in its environment, thereby fostering a connection with nature. This practical approach can help instill a sense of stewardship among participants, encouraging them to advocate for conservation initiatives.
Furthermore, educational outreach can involve collaboration with local communities. By involving citizens in research projects, conservation efforts can be amplified. Citizen science initiatives enable people to contribute valuable data to scientific studies, promoting communal engagement and awareness.
In summary, prioritizing research and educational programs in relation to the North American Pitcher Plant not only enhances scientific understanding but also cultivates a more informed public, essential for sustainable conservation efforts.
Future Directions in Research and Conservation
The North American Pitcher Plant, like many species in sensitive ecosystems, is facing numerous threats due to environmental changes and habitat loss. Understanding these challenges is essential for the future of conservation efforts. The field of research related to conservation strategies is broadening, and there are many innovative pathways that can be explored to protect the pitcher plant and its habitats. This section will delve into two critical areas: innovative conservation strategies and the potential for cross-disciplinary studies.
Innovative Conservation Strategies
Current conservation efforts often center around habitat restoration and protection. However, innovative strategies are vital to improve the chances of survival for the North American Pitcher Plant. One effective approach is the utilization of citizen science. Engaging local communities and enthusiasts can help gather valuable data on plant populations and their ecological health. Citizen scientists can monitor changes in pitcher plant habitats and contribute to a larger dataset that aids understanding of population dynamics.
Another significant strategy is the development of conservation corridors. These corridors can link fragmented habitats, allowing for the migration of species in response to climate change. Creating such pathways can help ensure genetic diversity and resilience among pitcher plant populations, which is essential for their survival.
Furthermore, integrating traditional ecological knowledge from indigenous peoples can enhance conservation efforts. Their understanding of local ecosystems can inform more sustainable management practices. This collaboration could improve overall ecosystem health and better protect the pitcher plant.
Potential for Cross-Disciplinary Studies
The significance of cross-disciplinary studies in conservation cannot be overstated. Fields such as ecology, genetics, climate science, and social science can contribute crucial insights into the survival of the North American Pitcher Plant. For example, genetics can reveal how pitcher plants adapt to various environmental pressures, allowing for targeted conservation strategies.
Moreover, climate science can assess how changing weather patterns might affect pitch plant populations. By modeling potential future scenarios, researchers can anticipate shifts in suitable habitats and make proactive conservation plans.
Social sciences, on the other hand, can address human factors that impact conservation efforts. Understanding the motivations and behaviors of communities surrounding pitcher plant habitats can lead to more effective engagement strategies. Engaging stakeholders from multiple sectors creates a more holistic approach to conservation.















